Eczema Treatment
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, a skin irritation characterized by red, flaky skin, sometimes with cracks or tiny blisters. It is extremely itchy and in some cases the affected areas of the skin can split and ooze clear fluid. If you have any itchy or flaky skin, don't scratch them as it may exacerbate the problem. Leave the area alone and seek medical attention immediately. The severity of eczema may vary from person to person.
In mild forms the skin would be dry, hot and itchy, whilst in more severe forms the skin can become broken, raw and bleeding may also occur. Though unpleasant, eczema is not contagious; the inflammation could be reduced through wide forms of treatments. Read up on different types of eczema and various treatment options.
Types of Eczema
- Contact eczema is a localized reaction and manifests as redness, itching, and burning where the skin has come into contact with an allergen or irritant.
- Allergic contact eczema is a type of eczema with red, itchy, weepy reaction where the skin has come into contact with a substance that the immune system recognizes as foreign. This can be caused by poison ivy or certain preservatives in creams and lotions
- Seborrheic eczema refers to a form of skin inflammation of unknown cause that appears as yellowish, oily, scaly patches of skin on the scalp, face, and occasionally other parts of the body
- Nummular eczema refers to a type of coin-shaped patches of irritated skin-most commonly on the arms, back, buttocks, and lower legs-that may be crusted, scaling, and extremely itchy
- Dyshidrotic eczema appears as irritation of the skin on the palms of hands and soles of the feet characterized by clear, deep blisters that itch and burn
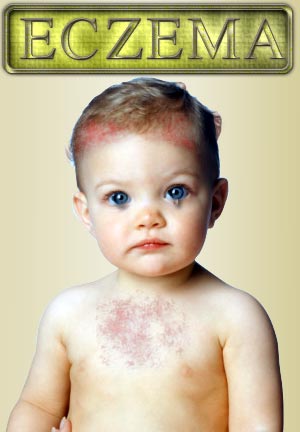
Baby Eczema
Infantile seborrhoeic eczema or cradle cap occurs both in children and adults. However, it is most common among infants between 2 months and 2 years of age. Infants affected by cradle cap or baby eczema are usually first are affected by this unpleasant form of skin condition. Normally this type of eczema will clear in just a few months, though the use of moisturizing creams and bath oils can help to speed this along.
Baby eczema may run in families that have a history of asthma or allergies. Infant eczema can also be aggravated by heat or irritants that come in contact with your baby's skin (like wool or the chemicals in some soaps, lotions, or detergents), by changes in temperature, and by dry skin. Infant eczema usually appears on a baby's forehead, cheeks or scalp, though it can spread to arms, legs, chest or other parts of the body.
The rash may begin as dry, thickened, scaly skin on the baby's body. In some cases it might be made up of tiny red bumps that can blister, ooze or infected if scratched. The treatment for infant eczema may include topical corticosteroids such as steroid creams and ointments. Your pediatrician may also recommend prescription medications that include antihistamines, oral or topical antibiotics.
Eczema treatment
There are various options for treating eczema though it can be completely cured. Antihistamines and topical immuno-suppressants help clear the affected area. Oral antibiotics may be used for skin infections that arise at the site of an eczema flare-up.
Topical steroids: This form of eczema treatment is resorted to when the skin is inflamed. The type and potency of topical steroid creams is prescribed on the age of the patient and severity of the condition. A thin layer of such creams is applied to affected parts of the skin.
Emollients: They reduce water loss from the skin and reduce dryness. Creams, ointments, lotions and bath oils help in re hydrating dry and cracked areas.
Oral steroids: Oral steroids are generally reserved for eczema that is resistant to all other treatments because this class of drugs is much more likely to cause side effects.
Phototherapy: UV A and B light therapy controls cells in the skin and thereby reduces scaling and sloughing of skin.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema or Pompholyx is a common type of eczema affecting the hands and sometimes the feet. This type of eczema is also called vesicular eczema of the hands or feet. This type of eczema is noticed to be seasonal. Some studies indicate that dyshidrotic eczema may be caused due to abnormal sweating. Dyshidrotic eczema is noticed mild peelings or severe big blisters and cracks that prevent you from working. At a more chronic stage, dyshidrotic eczema shows more peeling, cracking or crusting. Topical steroids and moisturizers may provide some relief. Oral anti-pruritics may help alleviate itching.
Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema is yet another type of chronic dermatitis characterized by coin-shaped, sharply demarcated lesions. As it develops, the lesions may resemble ringworms or fungus leading to a chronic condition. The cause of nummular eczema is unknown. The symptoms of nummular dermatitis include
- Itching
- Skin lesion that may be macules, papules, vesicles or patches
- Nummular lesions located on the arms and legs
- Scaly or excoriated (raw) skin
- Skin redness
Certain foods such as eggs, peanut butter, fish and eggs are known to trigger off eczema in children. Tight or rough clothing, sweating, harsh soaps and chemicals may also cause eczema attacks. Bathe immediately after swimming if you are prone to eczema or other forms of dermatitis. Apply moisturizer to prevent the skin from drying out.
Eczema Elidel
People suffering from eczema are treated with a variety of medications based on the diagnoses of skin conditions. If the medicine prescribed for eczema is not effective, your doctor may refer a steroid-free Elidel cream to relieve the symptoms of dermatitis formed on your skin. Studies indicate that elidel relieves the symptoms of redness, itching and inflammation caused by eczema.
It is recommended only for short or intermittent long periods of treatment. Elidel cream can be used on all affected areas of the skin, including face and neck. The use of Elidel for eczema is contraindicated for pregnant or nursing mothers. The most common side effects of Elidel on the skin are feeling of warmth on the skin, headache and cold.
Top of the Page: Eczema Treatment
Tags:#Eczema #eczema treatment #control eczema elidel #baby eczema #Cure for eczema #eczema cause #dyshidrotic eczema #eczema cream #nummular eczema #infant eczema
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Vitiligo Skin Disease - De-pigmented patches ...
Prickly Heat - Painful fallout of hot and humid summers ...
Narrow Band UVB - Used for skin conditions ...
Photodynamic Therapy - Combination of light and photosensitizing drugs ...
Mold Allergy - Reacting to mold spores ...
Latex Allergy - Reactions to soluble proteins in latex ...
Skin Fungus Infection - Itching and soreness ...
Eczema Treatment - Red, flaky skin, cracks or tiny blisters ...
Varicose Veins - Veins swell and rise above the level of the skin ...
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care

Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Top of the Page: Eczema Treatment
Popularity Index: 101,495

